Class Mammalia
Order Carnivora
Family Canidae
Borophagus diversidens—Bone-eating Dog // Canis—Wolves // Urocyon—Gray Foxes // Vulpes—Red Foxes
 Canids are, or were, prominent members
of the Carnivora in all parts of our region. Current or historic natives are Canis
latrans (Coyote), Canis lupus (Gray Wolf), Urocyon cinereoargenteus
(Gray Fox), Vulpes macrotis (Kit Fox), Vulpes velox (Swift Fox), and
Vulpes vulpes (Red Fox). Natural populations of Canis lupus were
extirpated from the area (though the Mexican Wolf has been reintroduced), and control measures have been aimed at Canis latrans,
though apparently with little lasting effect other than decreasing less wary,
non-target species such as Vulpes macrotis.
Canids are, or were, prominent members
of the Carnivora in all parts of our region. Current or historic natives are Canis
latrans (Coyote), Canis lupus (Gray Wolf), Urocyon cinereoargenteus
(Gray Fox), Vulpes macrotis (Kit Fox), Vulpes velox (Swift Fox), and
Vulpes vulpes (Red Fox). Natural populations of Canis lupus were
extirpated from the area (though the Mexican Wolf has been reintroduced), and control measures have been aimed at Canis latrans,
though apparently with little lasting effect other than decreasing less wary,
non-target species such as Vulpes macrotis.
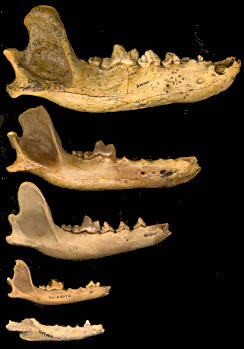
Fig. 1. Comparison of fossil dentaries of five species of canids. Top to bottom: Canis dirus (left dentary, reversed), Canis lupus, Canis latrans, Vulpes velox, and Urocyon cinereoargenteus. Larger images of the individual fossils can be seen in the species accounts.
Canids tend to be generalists and some engage in cooperative hunting. Most are active hunters rather than ambush predators. Plant food may be an important part of the diet. Differences in size and habit more or less divide up the prey pool, though there is some overlap within the family and between canids and felids.
Canids retain most of the primitive number of teeth, lacking only the third upper molars. The result in part is the presence of a long rostral region. Typical dentition can be seen at Stuff 2—the Stuff We Work With.
The bone-eating dogs were a subfamily (Borophaginae) of the Canidae, characterized by a short, broad skull with massive carnassials, giving rise to the belief that they were evolutionarily convergent with the Old World hyaenas (Kurtén and Anderson 1980).
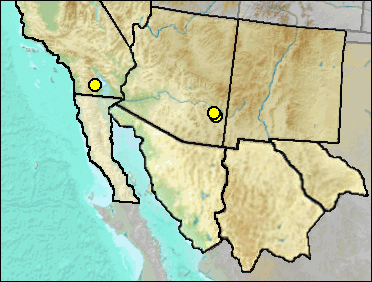
Sites.
Late Blancan: 111 Ranch (Morgan and White 2005); Anza-Borrego (Shaw and Cox 2006); San Simon Fauna (Morgan and White 2005).
Literature.
Morgan and White 2005; Shaw and Cox 2006.
Last Update: 28 Jul 2014