Class Aves
Order Accipitriformes
Family Accipitridae
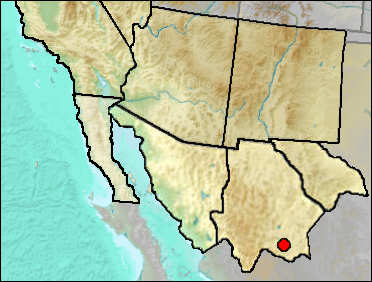
White et al. (2010) list Aquila from El Golfo, Sonora, but the listing of taxa by Croxen et al. (2007) does not include this taxon. It is possible that this is a later addition, but unless I can find the record elsewhere, I choose to not map it.
Sites.
Mid/Late Wisconsin/Holocene: Jimenez Cave (Messing 1986).
Literature. Croxen et al. 2007; Messing 1986; White et al. 2010.
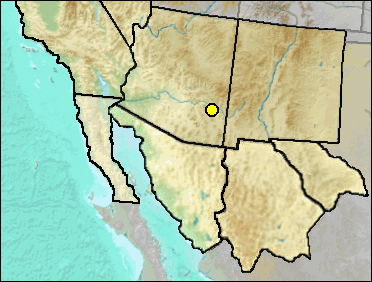
This is an eagle closely related to the Golden Eagle, but 10-20% larger than the females of that species (Emslie and Czaplewski 1999).
Sites.
Late Blancan: 111 Ranch (Emslie and Czaplewski 1999).
Literature. Emslie and Czaplewski 1999.
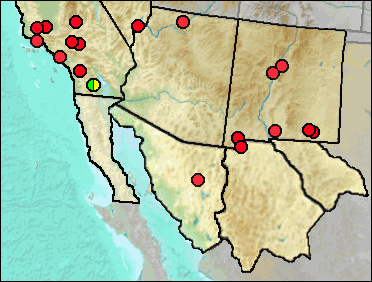
 Fig. 1. Aquila chrysaetos. Photograph by Donna Dewhurst, courtesy of the US Fish
& Wildlife Service.
Fig. 1. Aquila chrysaetos. Photograph by Donna Dewhurst, courtesy of the US Fish
& Wildlife Service.
It is assumed that only one species of Aquila occurs in our region during the Wisconsin. Golden Eagles are widespread in the West today and give little ecological information.
Although the specimens listed here by Harris compare well with Aquila, comparative material for Haliaeetus leucocephalus is not available.
Sites.
Late Blancan/Irvingtonian: Vallecito Creek, Anza-Borrego Desert (Howard 1963: ?).
Irvingtonian/Rancholabrean: Manix Lake (Jefferson 1991a).
Wisconsin: Carpinteria (Guthrie 2009).
Early/Early-Mid Wisconsin: Lost Valley (Harris 1993c: cf. gen.); Rm Vanishing Floor (Harris 1993c: ?).
Mid Wisconsin: McKittrick (Jefferson 1991a); Térapa (Steadman and Mead 2010); U-Bar Cave (Harris 1987).
Mid/Late Wisconsin: Dark Canyon Cave (Howard 1971); Diamond Valley (Springer et al. 2009); Hampton Court (Harris 1993c); Rampart Cave (Carpenter 2003); Rancho La Brea (Stock and Harris 1992).
Mid Wisconsin-Holocene: Shelter Cave (Howard and Miller 1933).
Late Wisconsin: Animal Fair 18-20 ka (Harris 1989); China Lake (Jefferson 1991a: cf.); Maricopa (Jefferson 1991a); Sandia Cave (Brasso and Emslie 2006).
Late Wisconsin/Holocene: Balcony Room (Harris 1993c); Conkling Cavern (Howard and Miller 1933); Howell's Ridge Cave (Howard 1962); Pendejo Cave (Harris 2003: cf. gen. et sp.); Isleta Cave No. 1 (Harris 1993c); Isleta Cave No. 2 (UTEP); Schuiling Cave (Jefferson 1991a); Stanton's Cave (Rea and Hargrave 1984).
Literature. Brasso and Emslie 2006; Carpenter 2003; Guthrie 2009; Harris 1987, 1989, 1993c, 2003; Howard 1963, 1962, 1971; Howard and Miller 1933; Jefferson 1991a; Rea and Hargrave 1984; Springer et al. 2009; Steadman and Mead 2010; Stock and Harris 1992.
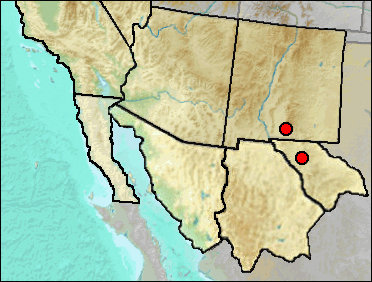
Although the specimens from the sites listed here compare well with Aquila, comparative material for Haliaeetus leucocephalus is not available, and the sites are not clearly distant from the habitat of the latter.
Sites.
Mid Wisconsin Pendejo Cave (UTEP).
Mid/Late Wisconsin/Holocene: Sierra Diablo Cave (UTEP).
Last Update: 15 Feb 2016