FAQ
Helpful information
What is the difference between CPU vs GPU?
| CPU | GPU | |
| Purpose | The CPU is often referred to as the “brain” of the computer. It handles all the general-purpose processing tasks. | Originally designed to handle rendering of images and video, GPUs are now also used for tasks that require parallel processing. |
| Architecture | Typically has a few cores (ranging from 2 to 64 in high-end models) designed for serial processing, meaning they handle tasks one at a time but very quickly. | Contains hundreds to thousands of smaller cores designed for parallel processing, meaning they can handle many tasks simultaneously. |
| Tasks | Ideal for tasks that require high interactivity and quick switching between tasks, such as running the operating system, and applications, and managing input/output operations. | Excellent for tasks that can be broken down into smaller, parallel operations, such as rendering graphics, machine learning, and scientific computations. |
| Latency / Throughput | Low latency, meaning it can quickly respond to individual tasks | High throughput, meaning it can process a large number of operations simultaneously |
| Use Examples | Running your operating system, browsing the web, and managing files. | Playing video games, rendering 3D models, and training machine learning models |
How are login nodes different from compute nodes?
In High Performance Computing (HPC) clusters, login nodes and compute nodes serve distinct purposes:
Login Nodes |
Compute Nodes |
|
| Purpose | Login nodes are the entry points to the HPC cluster. Users log in to these nodes to prepare their work. | Compute nodes are where the actual computational work is performed. |
| Functions | They are used for tasks such as editing scripts, compiling code, and submitting jobs to the scheduler. | They execute the jobs submitted by users from the login nodes. These nodes handle the heavy lifting of processing data and running simulations. |
| Access | Users can directly access login nodes via SSH. | Users do not log in directly to compute nodes. Instead, jobs are dispatched to these nodes by the scheduler. |
| Resources: | Typically have fewer resources compared to compute nodes, as they are not intended for heavy computational tasks. | Equipped with high-performance CPUs, large amounts of memory, and sometimes GPUs, designed to handle intensive computational tasks123. |
Workflow |
You log in, prepare your job script, and submit it to the scheduler. | The scheduler assigns your job to a compute node, where it runs until completion. |
What does 'sallac' command do?
The salloc command is used to allocate resources for a job within the SLURM workload manager.
Resource Allocation: salloc requests a set of resources (such as nodes, CPUs, and memory) from the SLURM schedule.
Interactive Sessions: It is often used to start interactive sessions, allowing users to run commands directly on the allocated resources.
Basic Command: salloc [options] [command]
If no command is specified, salloc will start a new shell on the allocated resources
SLURM (Simple Linux Utility for Resource Management) is a cluster management and job scheduling system that used in many of the world’s supercomputers and computing clusters.
- Resource Allocation: SLURM allocates exclusive or non-exclusive access to resources (compute nodes) for users to perform work.
- Job Management: It provides a framework for starting, executing, and monitoring jobs on the allocated nodes.
- Resource Contention: SLURM manages a queue of pending jobs and arbitrates contention for resources
- Scalability: Can schedule up to 100,000 jobs on large clusters.
Why is using containers with HPCs recommended?
1. Portability
- Containers encapsulate all the dependencies and libraries required by an application, ensuring it runs consistently across different environments
- Applications can be easily moved between different HPC systems or from development to production environments without compatibility issues
2. Reproducibility
- Containers help in creating reproducible research environments, which is crucial for scientific experiments and simulations
- They allow for precise version control of software and dependencies, making it easier to replicate and validate results
3. Efficiency
- Containers are more lightweight compared to traditional virtual machines, leading to lower overhead and better performance
- They enable better resource utilization by allowing multiple isolated applications to run on the same hardware without interference
4. Flexibility
- Users can create custom software environments tailored to their specific needs without affecting the host system or other users
- Containers support DevOps practices, enabling continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) workflows
5. Scalability
- Containers can be easily scaled up or down to meet the demands of different workloads
- They integrate well with cluster management and orchestration tools like Kubernetes, enhancing the scalability of HPC applications
6. Security
- Containers provide a level of isolation between applications, reducing the risk of conflicts and enhancing security
- They allow for controlled access to resources, ensuring that applications run in a secure and confined environment
How-Tos
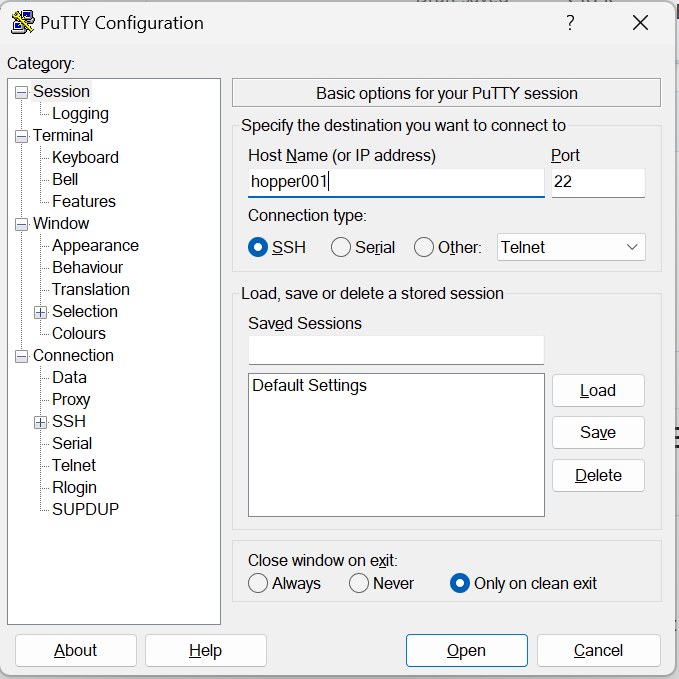
How to access the cluster using PuTTY?
1. Make sure you have Putty downloaded and installed: https://www.putty.org/
2. Open up Putty and you will be prompted with a dialog window (see below). Enter the host name: hopper001
3. You will be prompted to "login as", please enter your utep credentials username
4. You will be prompted to enter a password, please use your utep account password (when you type, the password you type will not be visible, don't worry, its a security measure)
5. You should be getting a message from the university about authorization and compliance (see below)
6. And you're in!
How to ssh into cluster using cmd line (Mac / Windows)
Before you start: Make sure you are either on the utep wifi or using the Utep VPN (global protect) to connect to the utep network.
WIndows 10 / Windows 11:
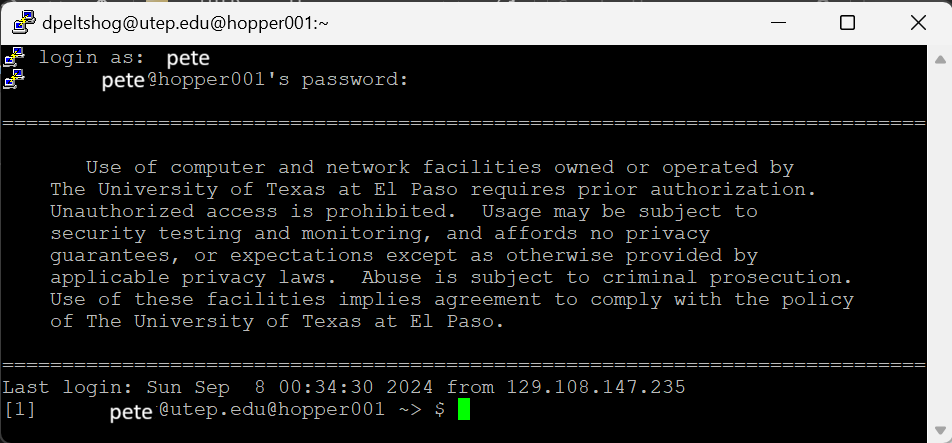
- Go to terminal (click Start Button or Search Button on the taskbar and search "cmd")
- In the terminal window (see below), type "ssh your-username@utep.edu@hopper001" (enter your utep username)
- You will be prompted to enter a password, please use your utep account password (when you type, the password you type will not be visible, don't worry, its a security measure)
- You should be getting a message from the university about authorization and compliance (see below)
- And you're in!
Mac OS:
- Bring up the terminal (search "terminal" in the Spotlight search function)
- In the terminal window, enter "ssh hopper001"
- You will be prompted to enter your username, use your utep credentials username
- You will then be prompted to enter a password, please use your utep account password (when you type, the password you type will not be visible, don't worry, its a security measure)
- You should be getting a message from the university about authorization and compliance (see below)
- And you're in!
How to transfer files using winSCP?
How to submit batch files in queue?




