Current Research
Impact Of Transborder Urban Growth Policies and Patterns on Ozone Concentration in the El Paso - Juárez Binational Region
This research examines the impact of urban growth policies and traffic patterns on ozone concentrations in the El Paso–Juárez binational region. Supported by the Air Quality Research and Development (AQRD) program, the project integrates land-use, transportation, and emissions modeling into a single analytical framework to better understand how cross-border urbanization affects regional air quality.
By expanding the El Paso UrbanSim land-use model to include Ciudad Juárez, researchers created a comprehensive binational platform that captures the interconnected dynamics of the two cities. Within this framework, the team evaluated alternative land-use and densification scenarios to assess how strategic planning could reduce vehicle miles traveled (VMT), traffic congestion, and ozone precursor emissions—including oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
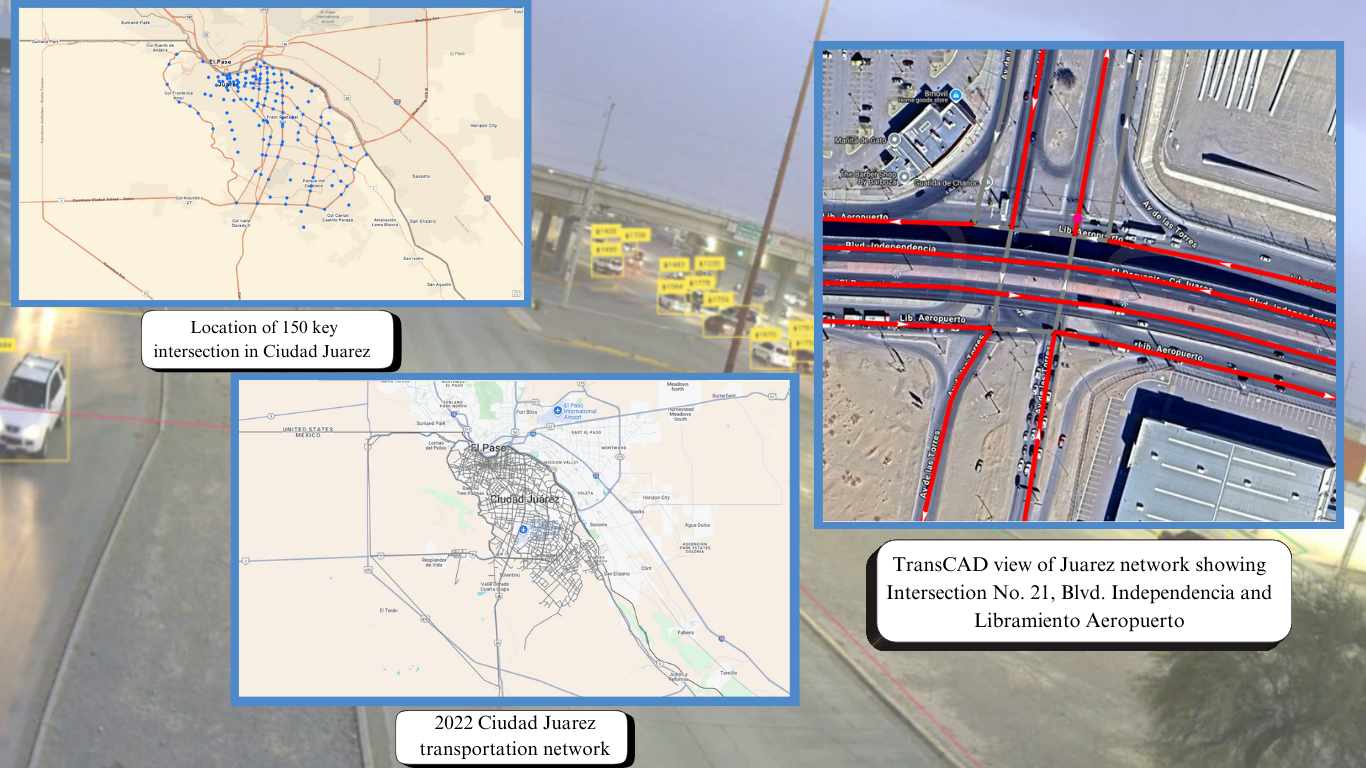
Using advanced analytical tools—UrbanSim, TDM, iTDM, STREAM, and BEEM—the study simulated scenarios for 2050 under various land-use and border-crossing conditions. Field data from over 150 traffic monitoring sites in Ciudad Juárez ensured model accuracy and realism.
Such targeted densification, mixed-use development, and enhanced transit connectivity may significantly reduce emissions by lowering automobile dependence and congestion. These findings provide a data-based foundation for a low-emission growth strategy that improves air quality and enhances livability throughout the El Paso–Juárez metropolitan region.
Project Details
Project Type: Research
Principal investigators: Dr. Cesar Tirado
Award Duration: 2024-2025




